
for incoming packet, type of packet and calling This task performs normal stack task including checking TFTPOpenFile(tftpFilePutName, TFTP_FILE_MODE_WRITE) TFTPServerAddr.Val = MY_DEFAULT_TFTP_IP_ADDR_BYTE1 | MY_DEFAULT_TFTP_IP_ADDR_BYTE2<<8ul | MY_DEFAULT_TFTP_IP_ADDR_BYTE3<<16ul | MY_DEFAULT_TFTP_IP_ADDR_BYTE4<<24ul This is how I`m tring to perform the operation: I modified TFTPGet to have the same interface like in UDPGet so function will looks like this: BOOL TFTPGet(BYTE *v) Get only first letter from file and then end of file. } Part of state machine you suggest looks like this: TFTP_RESULT res = TFTPIsGetReady () īreak Thanks to that I am able to read all file and find end of file and close connection(I verified that on wireshark).Network admins use TFTP Servers every day to transfer images, configuration files, firmware, etc. TFTP is simple on its own and does not need any sophisticated messaging to work. Of course, having no overhead is terrific, but there is a downside it does not provide any encryption and authentication mechanisms.Īlthough TFTP has no built-in security, network admins use it for simple and fast file transfers within LANs.Īnd best of all, it can be used for remote connections by hardening its security with the right server/client software.
Tftp client example how to#
In this step-by-step tutorial, you’ll learn how to set up and configure TFTP on Windows 10. We’ll learn how TFTP works, and how to set it up on the client and server. TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple file transferring mechanism developed as a “lighter” version of FTP. It attempts to over-simplify and downsize the functionality of FTP.
Tftp client example full#
Instead of using the full TCP implementation, TFTP relies on the connectionless and simple UDP transport over port 69. TFTP only allows unidirectional file transferring.
It provides zero control and has low overhead. The original idea of creating TFTP was to provide booting for disk-less computers or workstations that didn’t have enough memory or disk.
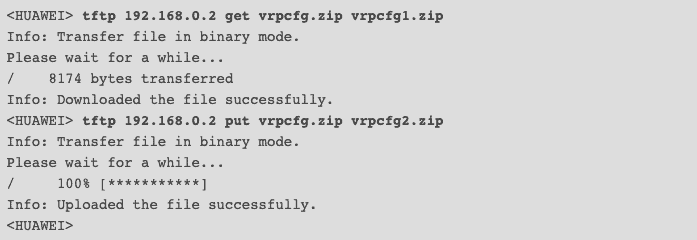
These disk-less workstations usually do not have access to the full TCP/IP stack, so they need to obtain configuration information such as DHCP or BOOTP from another server. TFTP uses a client/server communication model.Īs as you can see from the message exchange below, the TFTP server sends a block of data and waits for the acknowledgment before sending the next one.Ī host sends a Request to Write (WRQ), the server responds with an Acknowledgement (ACK), so the host sends data. The host can also send a Request to Read (RRQ) then the server sends the data and waits for an acknowledgment.
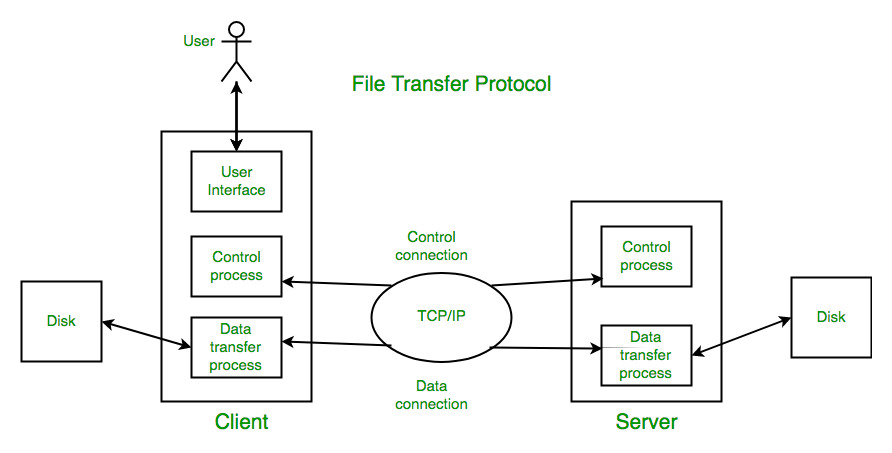
Today TFTP is commonly used for transferring configuration files and firmware images from and to networking devices. It is also used for network booting by diskless nodes that need booting from the LAN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
